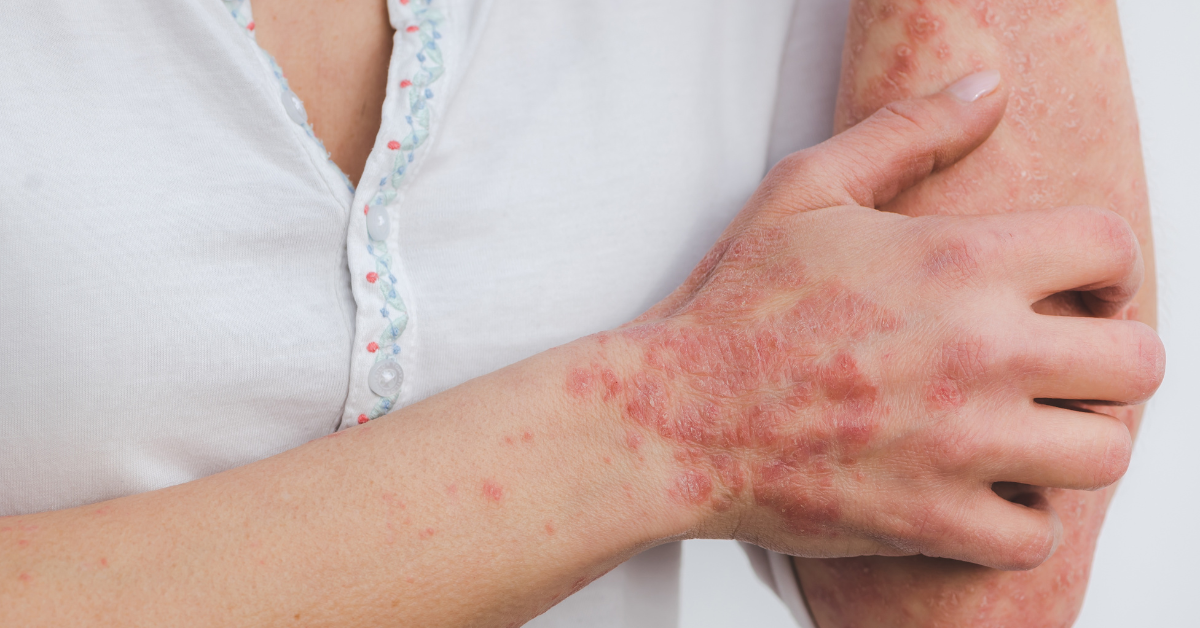
Psoriasis affects approximately 125 million people globally.
This is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. It is estimated to affect around 2-3% of the global population, with a higher prevalence in developed countries.
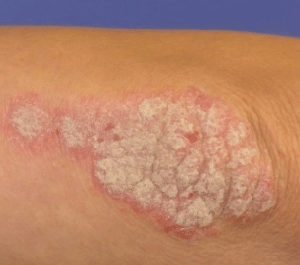
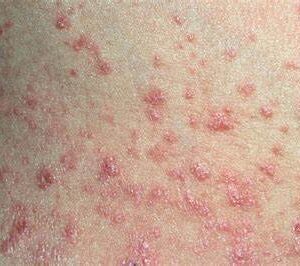
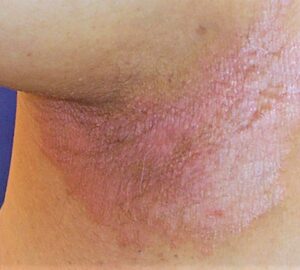
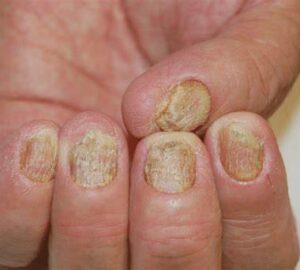
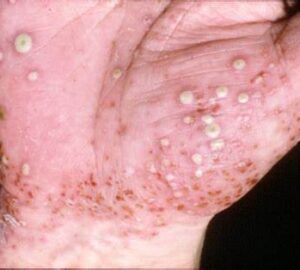
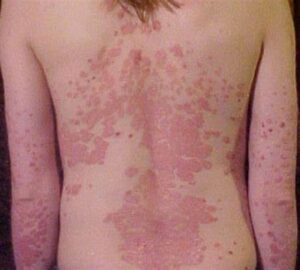
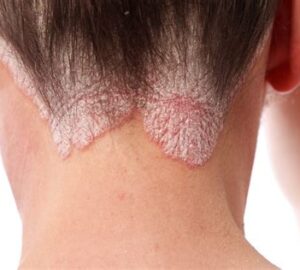
Psoriasis can affect any body part, but it most commonly appears on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. There are different types of psoriasis, including plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis etc.
In addition to the skin, psoriasis can be associated with an inflammatory arthritic condition known as psoriatic arthritis, a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects the joints and tendons. Psoriatic arthritis is estimated to develop in around 30% of psoriasis individuals.
This can significantly diminish one’s quality of life, often leading to physical discomfort, social stigma, and isolation. While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, treatments are available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Ayurveda offers time-tested remedies to manage the symptoms of psoriasis most effectively and safely.
Get A Call Back
Types of Psoriasis
Common Triggers Of Psoriasis

Stress: Can trigger a psoriasis flare-up or make existing symptoms worse. Stress can cause the immune system to become overactive, leading to inflammation and worsening psoriasis symptoms.
Infection: Such as strep throat or skin infections can trigger psoriasis symptoms or make existing symptoms worse. The body’s immune response to infection can lead to inflammation and worsening of psoriasis symptoms.
Weather Changes: Cold weather, dry air, and lack of sunlight can cause psoriasis symptoms to worsen. The dryness and lack of humidity in the air can cause the skin to become dry and irritated, leading to a psoriasis flare-up.

Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarial drugs, can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms.

Alcohol: Drinking alcohol can increase the risk of psoriasis flare-ups. Alcohol can cause the immune system to become overactive, leading to inflammation and worsening of psoriasis symptoms.
Smoking: Smoking can also increase the risk of psoriasis flare-ups. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can trigger inflammation and make psoriasis symptoms worse.
Skin Trauma: Injuries to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, and sunburns, can trigger psoriasis symptoms or make existing symptoms worse. The skin’s immune response to injury can lead to inflammation and worsening of psoriasis symptoms.
Causes Of Psoriasis, According To Ayurveda
Let’s look at the causes of psoriasis, according to Ayurveda:
- Inappropriate Diet: Irregular and unhealthy food habits, improper food combinations (Example: dairy products with fish or chicken), excessive intake of certain foods like yogurt, seafood, sour and salted items, alcohol etc. can contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
- Poor Digestion: According to Ayurveda, poor digestion can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the body, which can trigger psoriasis.
- Stress: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis in Ayurveda too. When the body is under stress, it produces more cortisol, a hormone that can trigger inflammation in the body.
- Exposure To Environmental Toxins: Exposure to environmental toxins, such as pollution and chemicals, can lead to an accumulation of toxins in the body, which in turn can trigger psoriasis.
- Family History According to Ayurveda, though psoriasis is prone to affect anyone with irregular food habits and lifestyle, someone with a family history is more probable to get affected by it.
Compilations Of Psoriasis
Is a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects up to 30% of people with psoriasis. It can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, and can lead to permanent joint damage if left untreated.
In one meta analysis, researchers has found an association between psoriasis and an increased risk of developing cancers.
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health, leading to feelings of depression anxiety and suicidal thoughts, as stated in this study.
People with psoriasis that covers 10% of their body or more are 64% more likely to develop diabetes than those without the condition, according to the study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis can affect the eyes, causing inflammation and dryness.These may include conjunctivitis (commonly known as pink eye), uveitis( an inflammatory disease of the eye), and blepharitis ( inflammation of the eyelid).
People with psoriasis have a higher prevalence of obesity compared to the general population, and obesity may worsen psoriasis symptoms. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that a higher body mass index (BMI) was associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
According to a review of various research studies, individuals with psoriasis are more likely to develop heart disease and experience risk factors linked to heart disease such as hypertension, high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes.
High blood pressure
Ayurveda perspective of psoriasis
Ayurveda manages psoriasis by addressing the underlying imbalances in the body that contribute to the condition. According to Ayurvedic concept, it is caused by an imbalance of all the three doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha) in varying degree, but predominantly Vata and Kapha.
The predominance of Vata causes dryness, pain, and scaling of the skin. Pitta imbalance causes redness, inflammation, and a burning sensation in the skin. Kapha vitiation causes rashes, itching, discharge, and thickening of the skin. This imbalance can be due to a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, lifestyle, and diet.
Ayurveda management of psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment in ayurvedic aims to balance the doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and remove the toxins from the body. Here are some best ayurvedic treatment for psoriasis:
- Ayurvedic Medications: Ayurvedic medications are used to reduce inflammation, to soothe the skin and address other health issues that may be associated with the condition.
- Ayurvedic Oil Massages: Ayurvedic oil massages, such as Abhyanga, can help moisturize and soothe the skin.
- Dietary Changes: dietary changes may involve avoiding certain foods that can aggravate psoriasis symptoms, such as spicy or acidic foods, and incorporating more anti-inflammatory foods into the diet.
- Lifestyle Changes: Ayurveda recommends lifestyle changes like practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga and meditation, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy sleep routine to help manage psoriasis.
- Panchakarma Therapy: Panchakarma is an Ayurvedic detoxification treatment that involves five different procedures to remove toxins from the body. In certain cases of psoriasis, this treatment may be advised.
It is important to note that Psoriasis Ayurvedic treatment should be taken under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic doctor.
Book Consultation in 3 Simple Steps

Schedule Your Online Consultation With Us Today!
♦ Request a Call Back ♦ Share Basic Info
♦ Pay Charges & Book ♦ Consult Doctor